Decoding Database Magic: The Art of Normalization for Cleaner Data and Smoother Operations
Understanding Database Normalization: Enhancing Data Integrity and Efficiency
In the world of database design, the concept of normalization is essential to database architecture since it guarantees data integrity, minimizes redundancy, and boosts overall effectiveness. This procedure optimizes database structures, laying a solid basis for efficient data management.
What is Normalization?
Normalization is the process of decomposing unsatisfactory (bad) relations by breaking up their attributes(columns) into smaller relations. Every stage of this procedure follows a set of guidelines called Normal Forms (NF), with the goal of removing anomalies and raising the database's overall quality.
Why Normalization?
1- Elimination of Redundancy
Take into consideration a denormalized table that holds client data. Customers who place several orders may receive redundant information from a single database that contains information about both the customers and their orders. Redundant data is reduced by dividing this into distinct tables for customers and orders, guaranteeing that each piece of information is stored only once.
Example:
Denormalized Table:
| Customer_ID | Customer_Name | Order_ID | Order_Date | Total_Amount || 001 | John Doe | 1001 | 2023-01-05 | $250 || 001 | John Doe | 1002 | 2023-03-12 | $150 || 002 | Jane Smith | 1003 | 2023-02-18 | $300 |After Normalization:
Customers Table:
| Customer_ID | Customer_Name || 001 | John Doe || 002 | Jane Smith |Orders Table:
| Order_ID | Customer_ID | Order_Date | Total_Amount || 1001 | 001 | 2023-01-05 | $250 || 1002 | 001 | 2023-03-12 | $150 || 1003 | 002 | 2023-02-18 | $300 | 2- Data Integrity:
By minimizing or removing inconsistencies that may result from redundant or contradicting data entries, normalization improves data integrity. Anomalies like as update, insert, or delete anomalies are prevented by it.
Levels of Normalization
There are different levels of normalization, or Normal Forms (NF), which range from the First Normal Form (1NF) to the Third Normal Form (3NF) and higher. A more sophisticated and effective database structure results from the specific data organization concerns that are addressed at each level.
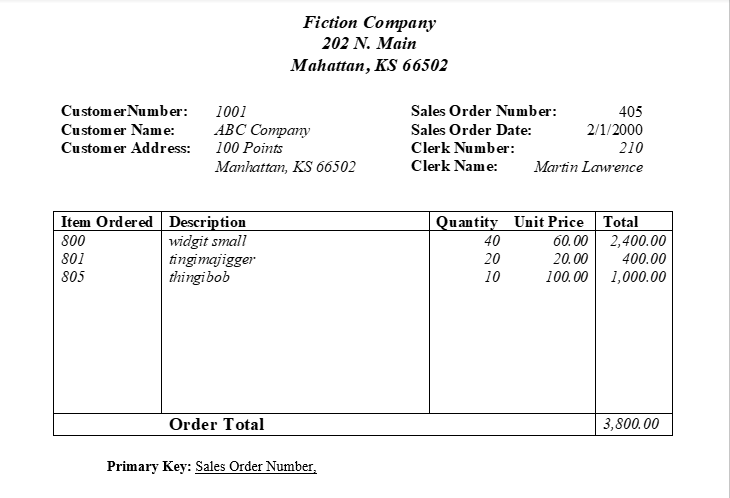
Normalizing a Sales Order Database: A Case Study
Imagine a database table called Sales Orders that contains duplicated data for every order, like item descriptions, clerk details, and customer information. By use of normalization:
Original Sales_Order Table (Denormalized):
After Normalization:
Sales_Order Table:
| Sales_Order_Number | | Sales_Order_Date | Clerk_Number (FK) | Customer_Number (FK) |Items Table:
| Item_ID | Item_Description | Unit_Price |Sales_Items Table:
| Sales_Order_Number | Item_ID | Quantity |Clerks Table:
| Clerk_Number | Clerk_Name |Customers Table:
| Customer_Number | Customer_Name | Customer_Address |Conclusion:
Normalization is an indispensable process in database design, facilitating efficient data organization, reducing redundancy, and enhancing data reliability. By adhering to normalization principles, databases become more manageable, scalable, and conducive to maintaining data integrity.
The significance of normalization extends beyond mere data structuring; it forms the bedrock of robust and efficient database systems, ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and scalability.